According to on-chain data, the rate of Ethereum’s supply reduction has reached its highest level in 2023.
As per an on-chain metric compiled by market tracker Glassnode, the ETH burn rate has reached 1.42%. This figure is the highest deflationary rate recorded since the instant spike of 17% in May 2022.
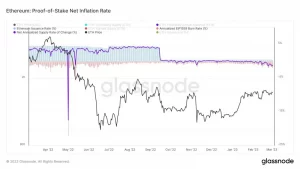
According to on-chain metrics from market tracker Glassnode, the Ethereum burn rate reached 1.42% as of late February 2023, which is the highest deflationary figure since May 2022, when it briefly hit 17% after the London hard fork upgrade. Prior to the upgrade, Ethereum had an inflationary model, but with the implementation of the Merge update, the rate of ETH issuance has dropped to zero.
Most crypto experts predict that the decrease in Ethereum’s supply will lead to long-term price increases. According to economic principles, when the supply of a product decreases while demand remains constant, prices will increase.
So, how exactly is Ethereum’s supply decreasing? In the Ethereum network, there are two different fees charged for each transaction. Firstly, the blockchain network charges a base fee for every transfer. In addition to this, those who want to complete their transactions more quickly can pay an additional fee.
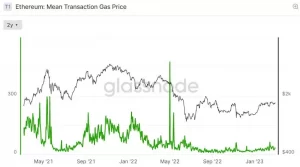
If network fees surpass Ethereum’s rate of increase, ETH supply decreases.
ETH Price
Ethereum, the biggest rival of Bitcoin, has lost 4% in value since the beginning of the week.
Since the second half of February, Ethereum has not been able to hold above the resistance level of $1,683, and after the recent selling pressure, it has dropped as low as $1,560.
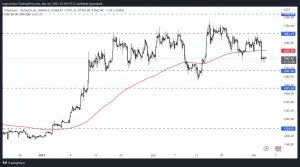
Possible supports for $ETH are located at $1,505 and $1,425 respectively. In order for the uptrend to continue, first, the 200-period moving average located at $1,600 and the resistance at $1,683 need to be broken.